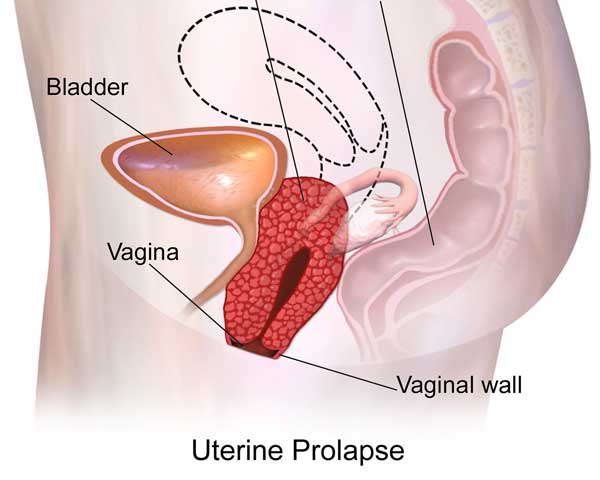
Uterine prolapse is a medical condition in which the uterus descends or slips into the vaginal canal due to weakened pelvic floor muscles and ligaments. This condition is more common in women who have gone through multiple pregnancies and childbirths. Here is a detailed overview of uterine prolapse:
Causes
- Childbirth: The stretching and weakening of pelvic floor muscles during childbirth can contribute to uterine prolapse.
- Aging: The natural aging process can lead to a gradual weakening of pelvic tissues.
- Weakened pelvic floor muscles: Factors such as obesity, chronic constipation, and heavy lifting can strain and weaken the pelvic muscles, increasing the risk of uterine prolapse.
Symptoms
Degrees of Uterine Prolapse
- First Degree: The uterus descends into the upper part of the vagina.
- Second Degree: The uterus descends to the opening of the vagina.
- Third Degree: The uterus protrudes outside the vagina.
Diagnosis
- Pelvic examination: A healthcare provider can diagnose uterine prolapse through a pelvic exam, assessing the degree of descent.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI may be used for a more detailed evaluation.
Treatment Options
- Conservative measures: Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles, lifestyle modifications, and weight management.
- Pessary use: A device placed in the vagina to support the uterus.
- Physical therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy to strengthen and tone the muscles.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases, surgical procedures like hysterectomy or repair of the pelvic floor may be recommended.
Prevention
- Regular pelvic floor exercises, especially after childbirth.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoiding heavy lifting and practicing good bowel habits.
Impact on Quality of Life
- Uterine prolapse can affect a woman's physical and emotional well-being, impacting daily activities and sexual function.
Seeking Medical Advice
- Women experiencing symptoms of uterine prolapse should seek prompt medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.