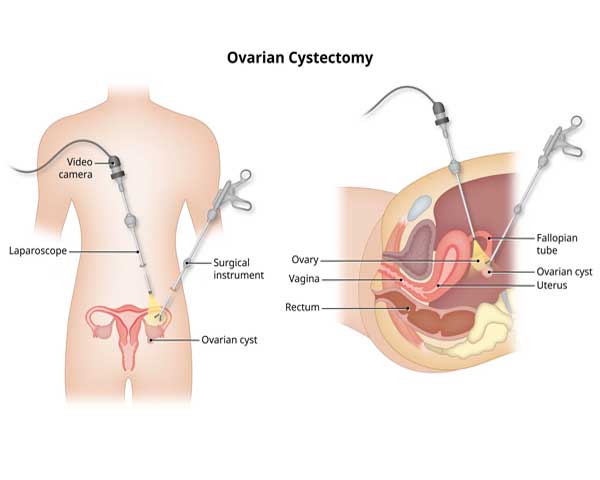
Ovarian cystectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove cysts that develop on the ovaries. These cysts can vary in size and may cause pain, discomfort, or other complications. The cystectomy is a common gynecological procedure aimed at addressing these issues. Here are the details about ovarian cystectomy:
Indications for Ovarian Cystectomy:
- Large Cysts: When cysts on the ovaries reach a significant size, causing pain or other symptoms.
- Persistent Cysts: Cysts that do not resolve on their own and persist over time.
- Complex Cysts: Cysts that appear complex on imaging studies and may have features raising concerns for malignancy.
- Symptomatic Cysts: Cysts causing symptoms such as pelvic pain, bloating, or menstrual irregularities.
- Infertility Concerns: In some cases, ovarian cysts may be removed to improve fertility, especially if they are affecting the normal function of the ovary.
Preoperative Assessment:
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound or other imaging studies are typically used to visualize the cyst and determine its characteristics.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess hormonal levels and rule out other conditions.
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial to understanding the patient's overall health and identifying any potential risks.
Procedure:
- Anesthesia: Ovarian cystectomy is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is unconscious during the procedure.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the lower abdomen, typically using minimally invasive techniques like laparoscopy. In some cases, an open abdominal incision may be necessary.
- Cyst Identification: The surgeon identifies the cyst and evaluates its characteristics.
- Cyst Removal: The cyst is carefully dissected from the ovarian tissue and removed. The goal is to preserve as much healthy ovarian tissue as possible.
- Ovarian Reconstruction: If the cystectomy involves a large portion of the ovary, the surgeon may perform ovarian reconstruction to preserve ovarian function.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples.
Postoperative Care:
- Recovery: Most patients can go home the same day or the day after the surgery.
- Pain Management: Pain medications are prescribed to manage postoperative discomfort.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are often advised to avoid strenuous activities for a certain period.
- Follow-up: Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing and assess any ongoing symptoms.
Risks and Complications:
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery.
- Infection: Risk of infection at the incision site or within the abdominal cavity.
- Ovarian Damage: In rare cases, there may be inadvertent damage to the ovary during the cyst removal.
- Scar Tissue Formation: Adhesions or scar tissue may develop in the abdominal cavity.
It's important to note that the specific details of an ovarian cystectomy can vary based on individual cases and the surgical approach chosen by the surgeon. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to discuss the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes based on their unique medical situation.