Menopause
Home / Menopause
Home / Menopause
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. It typically occurs in the late 40s to early 50s, and it is defined by the absence of menstrual periods for 12 consecutive months. Menopause is a significant life transition that involves hormonal changes and can bring about various physical and emotional symptoms. Here are key details about menopause:
Perimenopause: The transitional phase leading up to menopause is called perimenopause, which can start several years before menopause. During perimenopause, hormonal fluctuations can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and the onset of symptoms such as hot flashes and mood changes.
Hormonal Changes: Menopause is characterized by a decline in the production of estrogen and progesterone, two key hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. These hormonal changes can impact various aspects of a woman's health, including bone density, cardiovascular health, and reproductive organs.
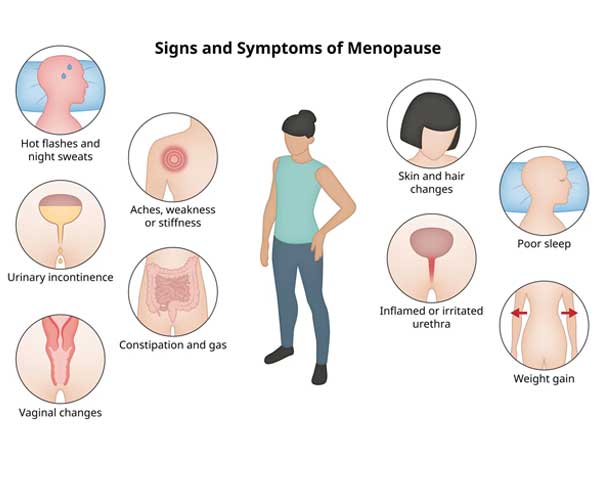
Common Symptoms:
Physical Changes:
Management of Symptoms:
Individual Experience: Menopause is a highly individualized experience, and not all women will experience the same symptoms or to the same degree. Some women may transition through menopause with minimal disruption, while others may find it challenging.
Post-Menopause: Once menopause is complete, and a woman has been without periods for a full year, she is considered post-menopausal. While many symptoms may diminish, it's essential to address ongoing health concerns, including bone health and cardiovascular health.
Regular Health Check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial during and after menopause to monitor overall health and address any specific concerns or symptoms.
Understanding and managing the physical and emotional changes associated with menopause are important aspects of women's health. Open communication with healthcare providers can help develop personalized approaches to address symptoms and promote overall well-being during this life stage.