Ectopic Pregnancy
Home / Ectopic Pregnancy
Home / Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical condition where a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop outside the uterus, typically in one of the fallopian tubes. In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg travels through the fallopian tube and implants itself in the lining of the uterus. However, in an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg gets stuck in the fallopian tube or implants in other areas such as the ovary, abdomen, or cervix.
Key points about ectopic pregnancy:
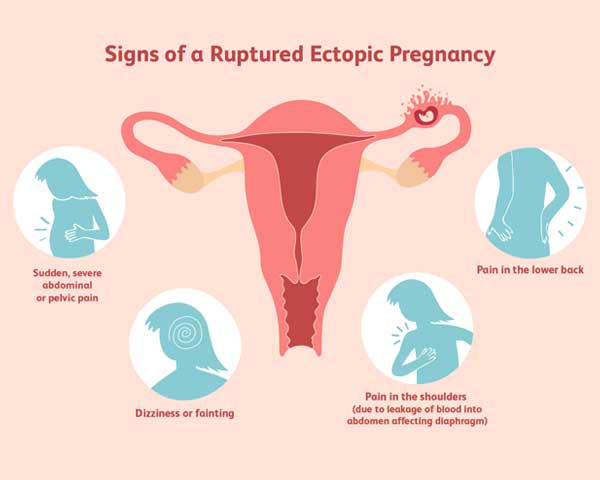
Symptoms: Ectopic pregnancy often presents with symptoms similar to early pregnancy, including missed periods, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, it may also cause abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding.
Risk Factors: Factors that may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy include a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), previous ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgeries, or conditions affecting the fallopian tubes.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically made through a combination of blood tests to measure pregnancy hormones (hCG levels) and imaging studies, such as transvaginal ultrasound, to locate the pregnancy.
Treatment: Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency, and prompt intervention is essential to prevent complications. Treatment options may include medication (methotrexate) to stop the growth of the pregnancy or surgical removal of the ectopic tissue.
Complications: If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can lead to a ruptured fallopian tube or other severe complications, such as internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening.
Future Fertility: The likelihood of future successful pregnancies depends on factors such as the extent of damage to the fallopian tubes. Many women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can go on to have healthy pregnancies in the future.
It's crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of ectopic pregnancy to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and intervention significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.